You’ve probably never thought about how sound can affect your stage set. Beyond trying to not create an environment that would drive the sound recordist mad, you usually don’t think about odd acoustic anomalies that might pop up that you never intended to happen. Like echoes.
Yeah, echoes will bite you in the ass if you’re not careful.
On the main set for the 1997 film Gattaca, just such an anomaly occurred, and it was the cinematographer who ended up saving the day.
And what does the cinematographer have to do with sound problems? Keep reading.
The Computer Hall set was designed by Production Designer Jan Roelfs and was inspired by the real-life location that he and Director Andrew Niccol chose for the film. The actual building chosen for the exterior of the Gattaca Aerospace Corporation was the Marin County Civic Center in California, designed by Frank Lloyd Wright. The art department flew to Marin and surveyed the interior details so that they could be matched for the set on stage, which was in a warehouse in Playa Vista.
The building they had leased made for an odd sound stage, but its size made it large enough to build the sets for the film in. There were the normal problems you deal with in a structure that was never designed to be a sound stage: support posts at regular intervals, a ceiling that is not nearly as high as those in an actual sound stage. On the plan below, you can see where the oval columns were designed to hide two of the building’s I-beam columns.
These are my drawings of the plan and elevations of the set with the areas of the sound problems circled.
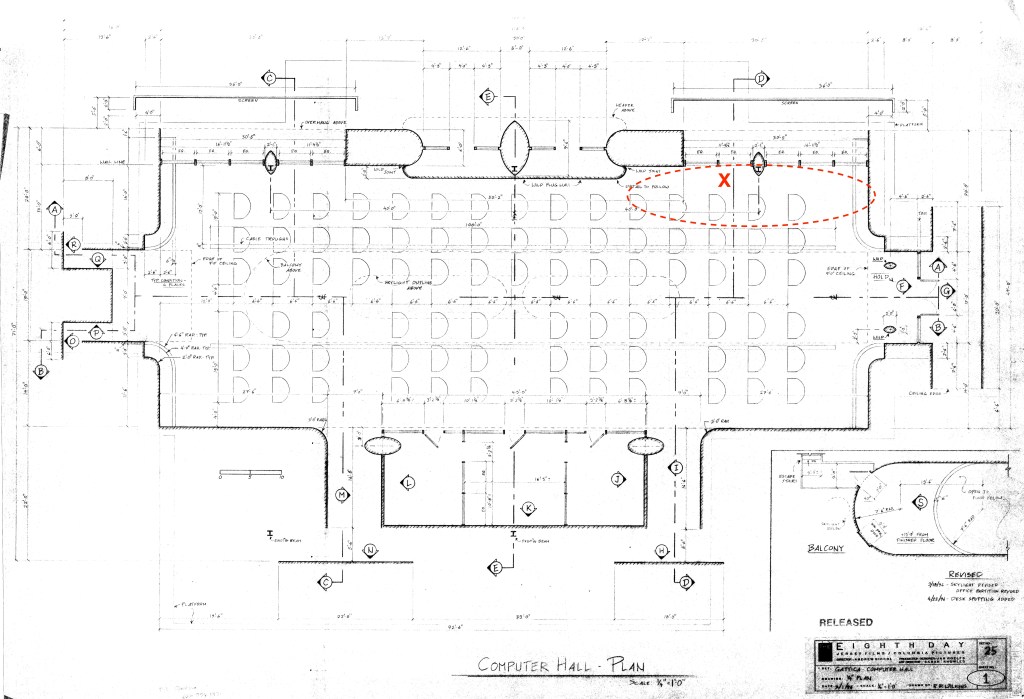
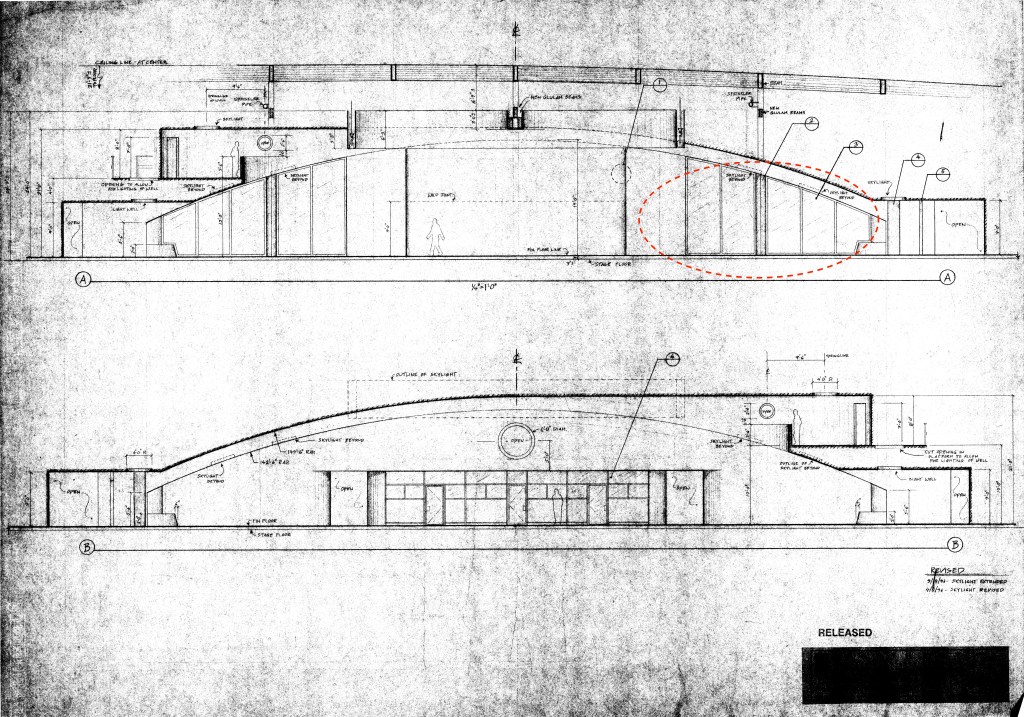
(One note: on the title block, you’ll notice it reads “Eighth Day”. This was the original title of the film. In pre-production, the producers learned that there was a French movie of the same name that was going to be released, and a name change was required. The writer and director Andrew Niccol decided that he would create a new title using the four letters used to identify the nucleobases of DNA: GATC.)
Turns out, theater designers had known about the sound reflective effects of elliptical and parabolic ceilings for years, as most of the western world designed theaters in the mode of the typical Italian horseshoe layout plan.
A presentation at the 2017 International Congress On Sound was focused on this phenomenon.
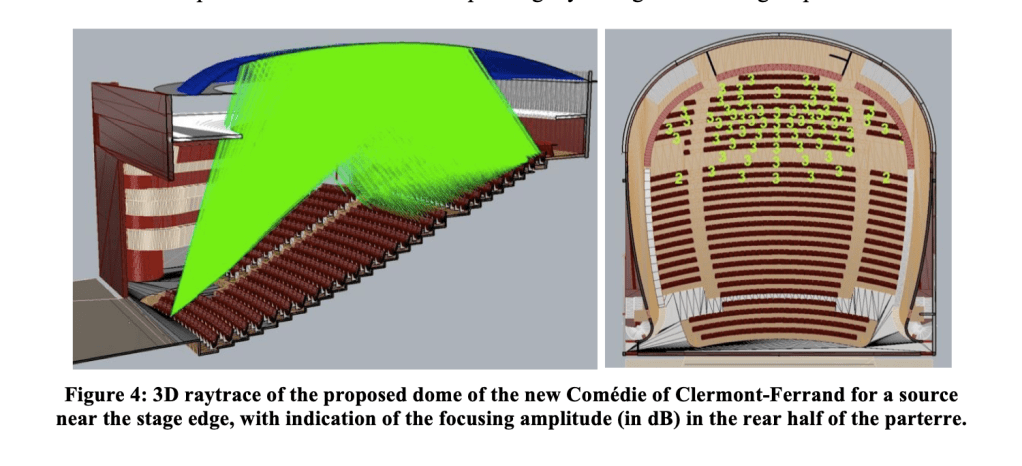
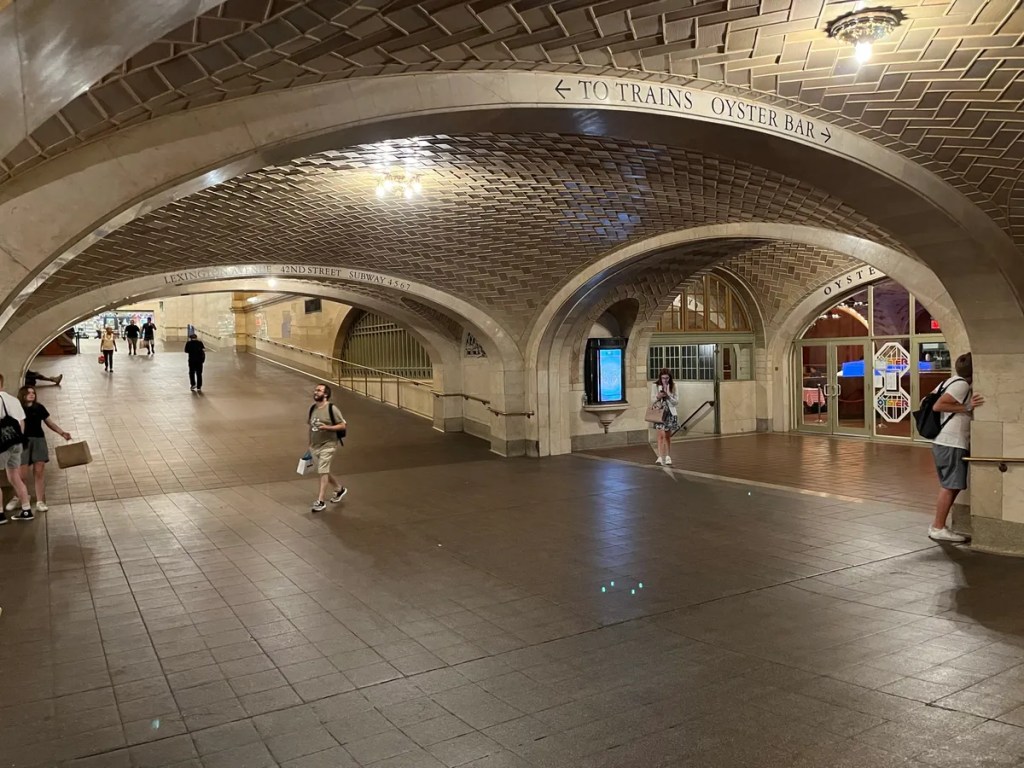
In New York City’s Grand Central Station, there is a ‘whispering gallery’ or acoustic vortex. This is an architectural phenomenon created by a number of configurations, in this case, a vaulted ceiling in the subway entrance under the terminal. A person standing in one corner of the hall intersection can whisper into the corner and the sound travels over the curved surface of the ceiling and can be heard by a person standing in the opposite corner.

I discovered the echo one day when I was walking the set and stopped at the point in question. I saw a gnat and clapped my hands together to kill it. That’s when I heard the strange echo. Horrified, I clapped again and there was the same echo. I clapped a third time, just as Jan was walking through the set. He stopped and frowned. “Don’t do that!’, he said.
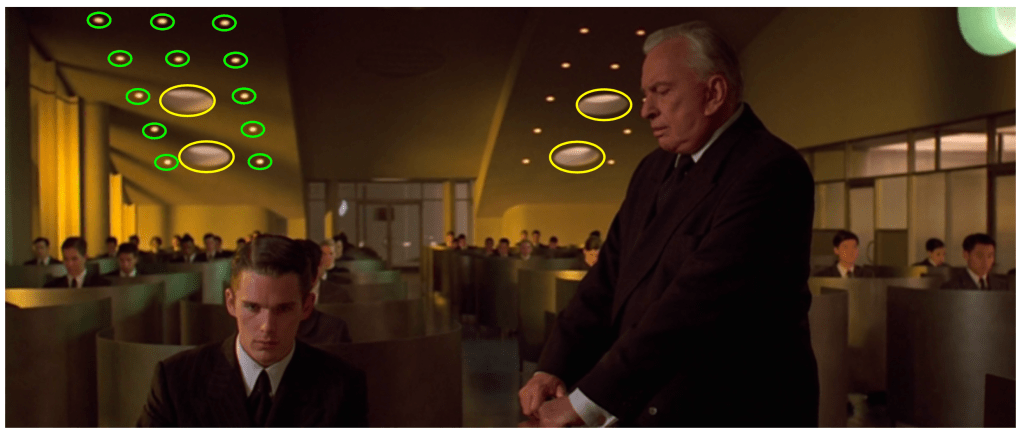
I think what was happening was that the area beneath the lower section of the ceiling of the set created a flutter echo, which was enhanced by the smooth ceiling surface. The two large skylights didn’t seem to affect this echo.
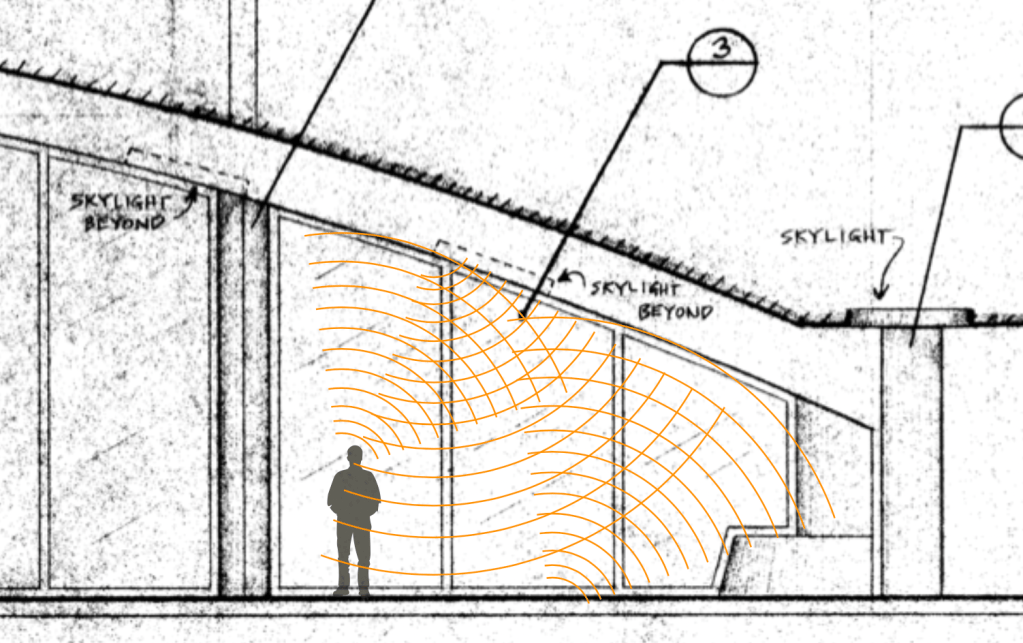
There was no carpeting or fabric to dampen the sound which would have eliminated this effect.
The solution came for the most part when the cinematographer, Slawomir Idziak, told us that he needed more practical lights in the set. This required creating dozens of new openings in the lower sections of the ceiling. These holes interrupted the acoustic waves and the echo disappeared. With the addition of the desks and the background actors, the sound reflection was minimal.
The photo below shows the original skylights in yellow, with the new lights circled in green.